Learning effectively is not just about spending hours studying; it’s about using the right strategies to maximize retention and understanding. Whether you’re a student, professional, or lifelong learner, these top 10 learning strategies will help you absorb and recall information efficiently.
1. Active Recall
Active recall is a powerful technique where you test yourself on the material rather than passively reviewing notes. It forces your brain to retrieve information, strengthening memory retention.
How to Use Active Recall:
- Use flashcards (e.g., Anki, Quizlet) to test yourself.
- After reading a chapter, close the book and summarize what you remember.
- Teach the concept to someone else or explain it out loud.

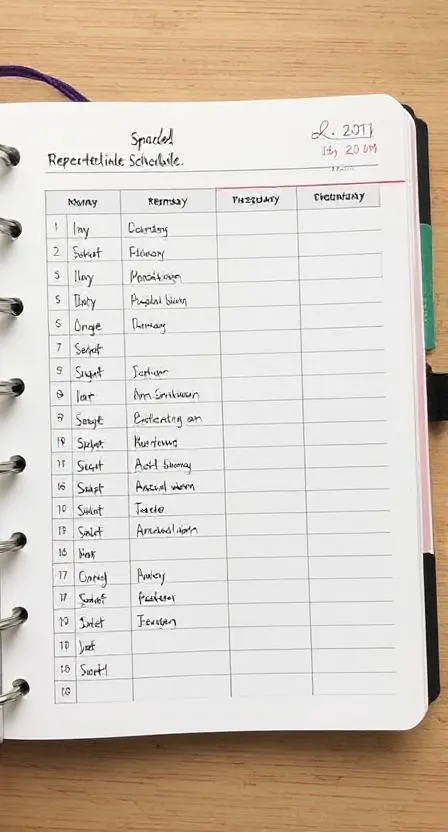
2. Spaced Repetition
Spaced repetition involves reviewing material at increasing intervals over time, ensuring better long-term retention.
How to Use Spaced Repetition:
- Study a topic today, review it in two days, then a week later, and so on.
- Use apps like Anki or SuperMemo that automate spaced repetition.
- Create a revision schedule incorporating spaced repetition techniques.
3. The Feynman Technique
The Feynman Technique is a simple yet effective way to understand complex topics by explaining them in the simplest terms possible.
How to Use the Feynman Technique:
- Pick a concept and write an explanation as if teaching a 5-year-old.
- Identify gaps in understanding and refine your explanation.
- Simplify further until you can confidently explain it without jargon.

4. Interleaving Practice
Interleaving is the practice of mixing different topics or types of problems instead of focusing on just one subject at a time.
How to Use Interleaving:
- Instead of studying one subject for hours, alternate between different topics.
- Mix problem types while practicing (e.g., solving algebra, then geometry, then physics problems).
- Create practice sessions that include multiple related concepts.

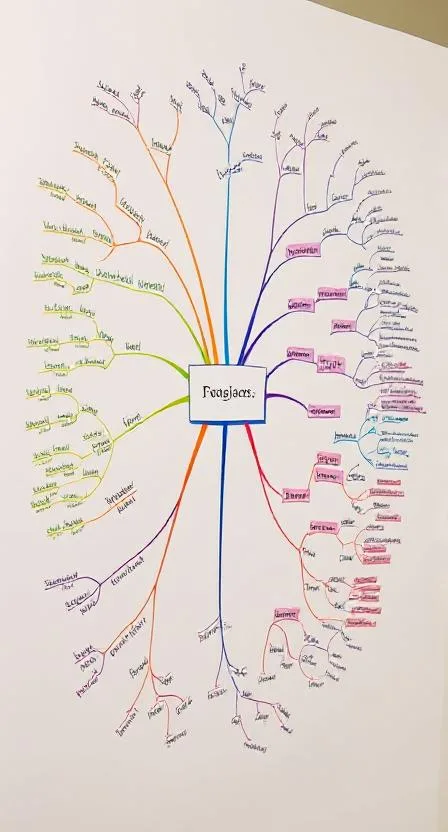
5. Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is a visual learning strategy that helps organize information and show relationships between concepts.
How to Use Mind Mapping:
- Start with a central idea and branch out with related concepts.
- Use colors, symbols, and images to enhance memory.
- Connect ideas logically to see the bigger picture.
6. The Pomodoro Technique
The Pomodoro Technique helps maintain focus and prevent burnout by breaking study sessions into short intervals.
How to Use the Pomodoro Technique:
- Study for 25 minutes, then take a 5-minute break.
- After four Pomodoro sessions, take a longer break (15–30 minutes).
- Use a timer or app to track your sessions.

7. Dual Coding
Dual coding combines verbal and visual learning to enhance understanding and retention.
How to Use Dual Coding:
- Pair written notes with diagrams, charts, or images.
- Convert textual information into infographics or concept maps.
- Watch educational videos that include both spoken explanations and visuals.

8. Self-Testing
Self-testing is an essential technique that reinforces learning by actively retrieving information rather than passively reviewing material.
How to Use Self-Testing:
- Use past exam questions or create your own quizzes.
- Test yourself before looking at your notes.
- Simulate exam conditions to improve recall under pressure.

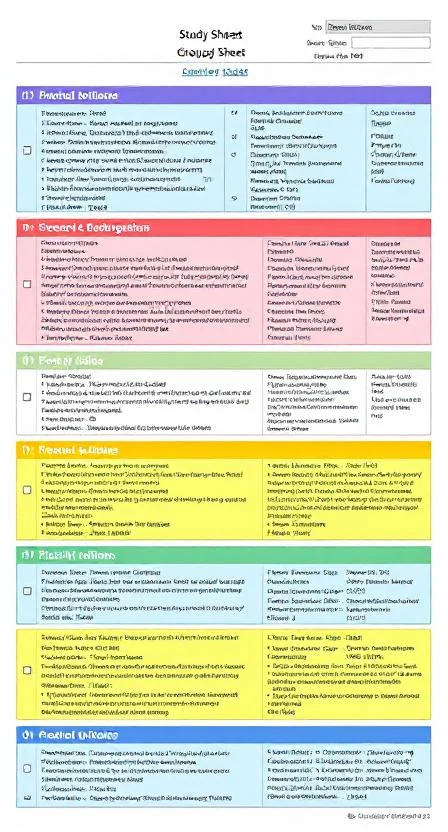
9. Chunking Information
Chunking is the process of breaking down large pieces of information into smaller, manageable units.
How to Use Chunking:
- Break long lists into smaller groups (e.g., remembering a phone number in sets of 3 or 4 digits).
- Categorize similar information into meaningful groups.
- Use acronyms or mnemonic devices to aid memorization.
10. Teaching Others
The best way to learn something is to teach it to someone else. This reinforces understanding and identifies gaps in knowledge.
How to Use Teaching as a Learning Strategy:
- Explain concepts to a study partner or friend.
- Create tutorial videos or write blog posts on what you’ve learned.
- Participate in group discussions and lead explanations.

Final Thoughts
Applying these learning strategies can significantly improve your ability to retain and recall information. Instead of passively reading or cramming, use techniques like active recall, spaced repetition, and mind mapping to make learning more effective. Try integrating multiple strategies into your study routine and see what works best for you. The key to long-term learning success is consistency, so keep practicing and refining your approach!
Which of these strategies have you found most useful? Let us know in the comments!




